What is Vitamin D?
Vitamin D is a fat soluble vitamin which is very important for a good bone structure as it regulates calcium and phosphorous metabolism in the body. The main source of Vitamin D is sunlight. The body can synthesize vitamin D in the body with the help of sunlight.
Physiology of Vitamin D
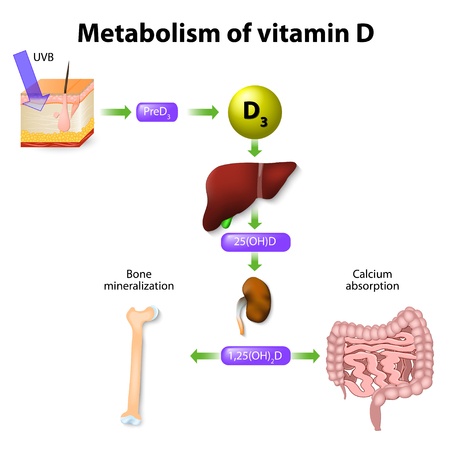
The active form of Vitamin D is called calcitriol (1,25-hydroxyvitamin D3). Vitamin D is synthesized when cholesterol on the skin is converted into calciol (vitamin D3). The vitamin D 3 then goes to the liver where it is converted into Calcidiol (25 hydroxyvitamin D3). This calcidiol is converted into the active form of Vitamin D in the kidneys.
Now that we have understood the regulation of Vitamin D, let us also know the sources of Vitamin D. It has been seen that people with darker skin tones and long term use of sunscreen can reduce the absorption of Vitamin D by the skin and lead to deficiency. In such cases vitamin D supplement and taking foods rich in Vitamin D is recommended.
Sources of Vitamin D
The main source of Vitamin D is sunlight. The average daily requirement of Vitamin D in adults is 600-800 IU. In infants and children the requirement is between 400-600 IU. There are dietary rich sources also. Eating these vitamin D foods will help you fulfill the body’s requirement of Vit D. Certain foods with Vitamin D are:
- Egg yolk
- Cod liver oil
- Mushrooms
- Tofu
- Cheese
- Beef liver
- Fortified foods like dairy products, juices, soy milk etc
- Fatty fish like tuna and salmon
Benefits of Vitamin D
Vitamin D is an essential vitamin in our body which helps our body structure (bones) remain strong, healthy and free from bone related diseases. Here are some of the health benefits of this vitamin that we should be aware about:
- Bones: Vitamin D is very important for the proper absorption of calcium in the intestines. Vitamin D deficiency can lead to rickets in children with softening of bones and curved legs. In adults the deficiency leads to osteoporosis making the individual more prone to fractures as the bony network is not strong enough. Osteoporosis is more commonly seen in post menopausal women.
- Pregnancy: Low levels of vitamin D during pregnancy are found to be associated with higher risk of preeclampsia and gestational diabetes. Hence all pregnant ladies are advised to take calcium and Vitamin D supplements.
- Cardiac Diseases: Vitamin D deficiency symptoms, based on researches has been associated with increased risk of cardiac diseases, hypertension and type 2 Diabetes. These conditions, further increase our health risks and also at times prove to be fatal with other complicated health conditions.
Deficiency of Vitamin D
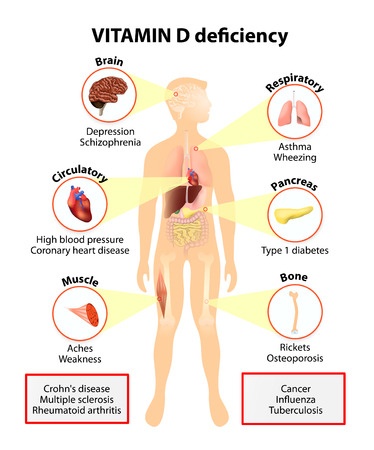
The following diseases are associated with deficiency of Vitamin D. The symptoms of Vitamin D deficiency are as follows:
- Rickets: Low levels of Vitamin D causes a poor absorption of calcium and phosphorous. Rickets is basically a childhood disorder and is seen more commonly in middle east countries and Africa. The reason why it is more common in infants is low levels of Vitamin D in breast milk and lack of exposure to sunlight. It is characterized by bowing of legs and weak and deformed bones.
- Osteomalacia: It is a disease that results from deficiency of Vitamin D in adults. It is characterized by softening of bones, bowing of legs, muscle weakness and weak bones leading to increased risk of fractures.
- Other Conditions: Apart from the above two, vitamin d deficiency can also lead to a weakened immune system, depression, autoimmune diseases, cancer, skin problems like eczema and dementia.
Vitamin D Side Effects
The side effects of Vitamin D are not very common and are likely to occur only when high dose supplementation is done. The normal upper limit of Vitamin D levels in the body is 4000 IU/day.
- Pregnant women and breast feeding mothers need to be very careful about over dosage of Vitamin D as it can lead to hypercalcemia and cause serious harm to the fetus in the form of a syndrome with mental retardation and facial deformities.
- High levels of vitamin D in people with a pre-existing kidney disease, where the kidney is unable to regulate the normal levels of calcium and phosphorous proves harmful. It can lead to renal osteodystrophy.
- Hyperparathyroidism patients can develop vitamin d toxicity by long continued use of supplements.



