What is Sleep Apnea?
Sleep apnea is basically a sleep disorder and is considered to be serious as it affects the breathing of the person. The disorder is characterized by shallow breathing or a complete pause in the breathing during sleep. As a result, the person awakens with a start gasping for air. Each episode may last for a few seconds to minutes. It can happen multiple times in the same night and almost each time the episode is preceded by loud snoring. The sudden waking up during sleep many times a night leaves the person tired and dizzy in the morning. In school going children it can cause hyperactivity and difficulty in concentration.

Types of Sleep Apnea
There are three types of sleep apnea. The classification is on the basis of the cause and presentation of the disorder.
- Obstructive Sleep Apnea: OSA or obstructive sleep apnea occurs because of the blockage of the respiratory passage when the tongue falls backward in the mouth during deep sleep.
- Central Sleep Apnea: Central sleep apnea occurs due to an instability in the respiratory center due to which the brain fails to get the stimulation for contraction of respiratory muscles. There is no blockage of the respiratory passage by the tongue like OSA.
- Mixed Sleep Apnea: This type of sleep apnea presents with symptoms of the above two types and both the causative factors play a role here.
Risk Factors For Sleep Apnea
It has been seen that sleep apnea can affect adults as well as children. The following are some identified risk factors for sleep apnoea
- Males are more often affected than females
- Age group above 40 yrs
- Over weight
- Having a short neck
- Large neck size (greater than 16-17 inches)
- People with a large tongue or jaw size
- Nasal polyps, adenoids or deviated nasal septum
- GERD-gastro esophageal reflux disorder
- Family history of obstructive sleep apnea
Signs and Symptoms of Sleep Apnea
- Presentation of an episode of Sleep Apnea:
- Loud snoring
- Shallow breathing or stoppage of breathing in sleep.
- Sudden waking up at night, gasping for breath.
- Dryness of throat
- Chocking or blocked sensation in the throat
- Insomnia
- Restless sleep with multiple interruptions
- Feeling tired in the morning
- The frequent waking at night is responsible for impaired alertness during the day. Inability to carry out day to day activities may be noticed in people who have episodes of sleep apnea on a regular basis.
- Vision problems may occur in some people
- Driving may become difficult
- Sleep apnea depression is also commonly seen.
- Work related accidents may increase due to reduced mental alertness
- In students, attention and concentration at school may become difficult
- Many young patients exhibit hyperactivity due to lack of sleep.
- Chronic sleep apnea can lead to heart troubles and a deranged liver function.
- Untreated severe sleep apnea can even lead to death due to lack of oxygen to the brain.
- Presentation of an episode of Sleep Apnea:
Diagnosis of Sleep Apnea
The typical presentation of the symptoms along with increased day time tiredness and sleepiness normally raise the doubt towards the diagnosis of sleep apnea. The diagnosis can be confirmed with the help of a formal sleep study also called as a polysomnogram. The test electronically records the activity level during sleep. The results are then analysed by a sleep specialist. The study can give the finer details of the problem like the number of events per hour. The diagnostic criteria for sleep apnea is as follows:
- Mild OSA– number of events ranging between 5 to 14 per hour
- Moderate OSA- number of events are 15-29 per hour
- Severe OSA-patients having more than 30 events in one hour
A pulseoximeter may be attached to the finger of the patient in order to study the fall in the oxygen levels during sleep. It can demonstrate or indicate the time of the episode of the sleep apnea.
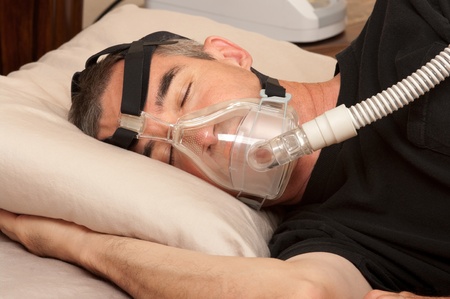
Treatment of Sleep Apnea
- Mild cases of obstructive sleep apnea can be treated at home by the following changes in the diet and the life style. They are:
- Stop smoking as smoking tends to cause swelling in the upper airway and increases the chances of snoring and apnea.
- Avoid alcohol consumption
- Loose weight and attain an ideal BMI
- Avoid sleeping on the back. Sleeping on the side can reduce the number of the apnea episodes. Changing sides frequently also helps some patients.
- Do not take sleeping pills
- CPAP: Another treatment for sleep apnea is the use of CPAP-continuous positive airway pressure. This is basically a cpap mask that is worn on the face covering the nose and mouth and it is attached to a CPAP machine that provides a continuous air flow into the nose. The air flow works by keeping the respiratory passage open and so breathing continues normally. CPAP therapy for sleep apnea is one of the most common mode of treatment.
- Surgery: If the sleep apnea is associated with other problems like nasal polyps, adenoids or a small jaw causing the throat to be very narrow, then corrective surgery will help in reducing the symptoms of sleep apnea. Surgery for deviated septum sleep apnea is very effective.
- Another recent invention for those people who cannot use the CPAP is a device called Inspire which is a small implanted device that acts as an upper airway stimulator.
Complications of Sleep Apnea
The following are some disorders associated with cases of sleep apnea:
- Stroke
- Heart failure
- Irregular heart beats
- Depression
- Diabetes
- Headaches
- Rise in blood pressure

