About Polio
Polio is the commonly used term for poliomyelitis or infantile paralysis. It is an infectious disease that is caused by polio virus. The most characteristic symptom is the weakness and paralysis of the lower extremities. In a small percentage of cases there is a complete inability to move. The muscles that are most commonly involved are those of the legs but occasionally muscles of the head, neck and diaphragm are also affected. It is seen more often in children below the age of 5 years. A vaccine was developed against the disease in the year 1953 and was put in use in 1957. The success of the polio vaccination has lead to a steady downfall of the incidence of polio and some of the countries like America, Europe, Western Pacific and Southeast Asia were declared as polio free.
Aetiology and Transmission of Polio
Poliomyelitis is caused by an enterovirus organism called poliovirus. This organism proliferates in the throat and the gut. Polio is a contagious disease and spreads via the feco-oral route by consumption of contaminated food and water. The incidence peaks in the summer and autumn seasons. The incubation period is between 6-20 days. This is the time taken between the first exposure and the first appearance of symptoms.
Predisposing factors that increase the risk of the disease are malnutrition, immune deficiency, pregnancy and skeletal muscle injury.
Symptoms of Polio
It has been seen that 95% cases of polio are asymptomatic and usually tend to resolve on their own. But in spite of the absence of symptoms, the person is infective and can spread the disease. The polio symptoms are broadly of two types:
- Non-Paralytic Polio: Signs and symptoms of this type can last for upto 10 days and the symptoms are fatigue, sore throat, headache, vomiting and meningitis.
- Paralytic Polio: 1-5% of the cases develop paralytic polio which affects the brain stem and the spinal cord. The initial symptoms are similar to the above type but gradually more severe symptoms appear like:
- Muscle spasms and pain
- Weakness of the legs or floppy limbs
- Sudden onset of paralysis
- Loss of reflexes
- Deformed limbs
- Post Polio Syndrome: After a person recovers there are some symptoms that may linger on like weakness of limbs, muscle pains, difficulty in breathing, weakness that is spreading to other muscles of the body and depression. This syndrome is seen in 20% of the people who have survived polio.
Diagnosis of Polio
The diagnosis of polio disease is done on the basis of symptoms and clinical examination. The doctor will look for neck stiffness, muscles weakness and reflexes. Laboratory investigations stool examination, throat swab and cerebrospinal fluid testing may be done.
Treatment of Polio
There is no treatment for polio and the patients are offered only symptomatic relief. The main stay of treatment is to relieve pain and hasten the recovery process. Medicines like painkillers, anti inflammatory drugs for inflammatory arthritis treatment, antibiotics to take care of the infections and anti spasmodic drugs for cramps and muscles aches are commonly prescribed. Physical therapy or occupational therapy plays a very important role here as it can be used to reduce pain, increase muscle strength and help in walking. Breathing problems and lung endurance can be taken care of by pulmonary rehabilitation. Advanced cases where the patient is unable to walk may need leg polio braces, orthopedic surgery or wheelchair assistance.
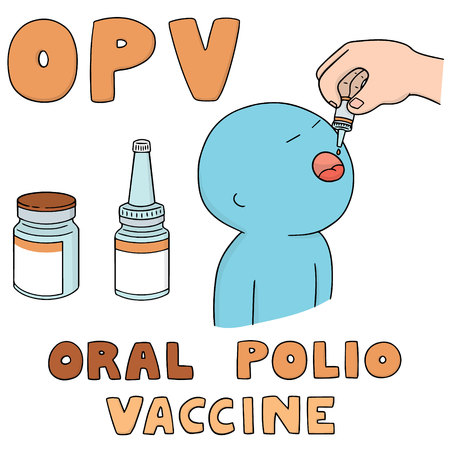
Polio Vaccination
The best way to avoid the disease is to get your child vaccinated for polio. There are two types of polio vaccination available. OPV is oral polio vaccine which is the easiest and most effective way to take care of the disease. Two drops of the vaccine are put into the mouth of the baby. The dosage is at birth, 6 months, 9 months and a polio booster vaccine dose at 5 years of age.
IPV is also known as Salk vaccine or inactivated polio vaccine. It is in the form of an injection. The immunization polio shots are given at 6 weeks, 10 weeks and 14 weeks. Most of the people who received three doses of IPV vaccine showed 99% immunity to the disease.
A strict immunization schedule has ensured that many countries have become polio free. The virus is known to be active in some countries like Afghanistan and Africa. When travelling to these countries, travel vaccinations, and others are mandatory to protect yourself with these immunization shots. The polio vaccination drives are on to cover maximum possible children under the age of 5 and get them vaccinated.
