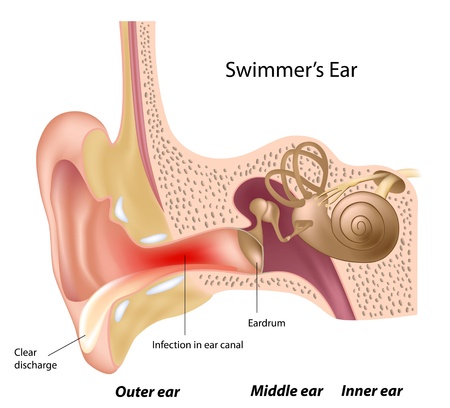
The anatomy of the ear is divided into three parts: the external ear that comprises of the ear lobe or pinna, the middle ear that includes the auditory canal, the ear bones, Eustachian tube and the eardrum, lastly the inner ear that hold the cochlea and the vestibular apparatus which are responsible for maintaining balance and equilibrium. Ear infections refer commonly to middle ear infection. They tend to be painful because of the inflammation and collection of fluid in the ear canal. Ear infections can be acute and chronic in nature. Acute infections tend to get cleared up very soon whereas chronic infections have a longer course as patients keep getting intermittent flare ups. The chronic ear infections tend to damage the middle and inner ear.
Causes of Ear Infections
The commonest cause of ear pain is the infections, swelling and collection of fluid in the Eustachian tube which runs from the middle ear to the posterior part of the throat. The Eustachian tube gets blocked by:
- Allergies
- Hay fever
- Common cold
- Tobacco consumption
- Smoking
- Swollen and infected adenoids
- Throat infections
- Fluid in ear in case of swimmers (swimmers ear)
There are some other risk factors that lead to infant ear infection.
- Altitude changes
- Changes in the climate
- Cigarette smoke
- Pollution leading to constant cough
- A recent illness
Ear Infection Symptoms
The ear infection symptoms in infants will stay the same as that in adults, except the fact that kids don’t know how to express the distress like adults.
- Mild to moderate pain and discomfort in the ear
- Feeling of pressure or a blocked sensation in the ear.
- Rubbing the ear and fussiness are the classical signs of ear infection in infant.
- Pus like thick yellow discharge
- Difficulty in hearing or deafness in chronic cases
- Fever that goes till 102 degrees.
- In chronic ear infections the symptoms tend to be come and go and usually affect both the ears.
Diagnosis of Ear Infections
The symptoms of ear pain and fever point towards an infection. The diagnosis is confirmed with the examination of the ear with an instrument called the otoscope which has a light and a magnifying glass and enables the doctor to see the middle ear nicely. Presence of a foreign body, fluid in the middle ear, redness, bulging or perforation of the ear drum are some of the common findings on examination of ear diseases.
Ear Infection Treatment
Most of the ear infections are mild and tend to clear up on their own. If the infection is sever and associated with fever, then medications like pain killer and antibiotic pills or antibiotic ear drops will be required. If the ear pain is due to an existing cold, then decongestants and anti allergic medicines will provide effective results as the swelling in the Eustachian tube will decrease. In bacterial infections with a pus like discharge, antibiotics will be required to control the infection and prevent it from spreading to the inner ear. If the infection is very severe, then the nerve gets involved and it can lead to hearing loss.
If medical treatment is not effective then surgery may be needed. Tubes may be placed in the ear to drain out the fluid collected. If adenoids are causing repeated infections, then surgical removal of the adenoids is indicated.

Ear Infections in Infants and Babies
The reason why ear infections are common in babies and toddlers is that their Eustachian tube is shorter and so the infection travels much faster. When you see a baby with ear infection, it could be because of bottle feeding. Bottle fed babies have a greater risk of developing an ear infection as compared to a breast fed baby. Another important reason of ear infections in babies that is often missed is the use of a pacifier. The pacifier acts as a source of infection if it is not properly sterilized and the infection travels from the mouth to the throat and the ear.
The best way out here is to take utmost care of the hygiene and avoid these infections. Wash your hand often. When using bottles for your baby, you must always sterilize them properly. Also sterilize the pacifier so that it does not become a source of infection for the child. Encourage breast feeding and give all the vaccinations on time.
Some other general methods of prevention are avoiding over crowded places and cigarette smoke. Even passive inhalation of the smoke is dangerous for you and your children. Be very cautious that your toddler does not put any object inside the ear as it can get stuck up and even rupture the ear drum.