What is Dysarthria?
Dysarthria is a motor disorder of the speech. This neurological deficit occurs as a result of injury to the motor component in the speech system. The muscles of the tongue, lips, mouth, vocal cord and diaphragm are required to work in coordination for normal speech to form. In dysarthria this muscle coordination is lost and so the speech is abnormal and difficult to understand. The severity of the problem will depend on the extent of damage in the brain. It is not a very common disorder and is known to be affected with certain types of neurological disorders.

Causes of Dysarthria
The following medical conditions and disorders affect the area of the brain that controls the motor functions like contraction and coordination of skeletal muscles. Depending on the part of the brain affected, there will be other symptoms along with dysarthria.
(a) Degenerative Disorders
- Parkinsonism
- Multiple sclerosis
- Huntingtons disease
- Amyotopic lateral sclerosis
(b) Toxic and Metabolic Causes
- Wilsons disease
- Hypoxic encephalopathy
- Central pontine myelinolysis
(c) Traumatic Brain Injury
(d) Thrombosis or Embolism in the brain which leads to a medical condition called stroke
(e) Brain Tumor
(f) Cerebral Palsy
(g) Gullian Barre Syndrome
(h) Hypothermia
Symptoms of Dysarthria
- In dysarthria, the muscles of the tongue, lips and the vocal cords fail to work in proper coordination and so it will first affect the quality of the voice. The voice generally becomes hoarse and heavy like the one associated with a cold.
- Chewing and swallowing is also difficult
- Saliva does not move around in the mouth properly and the muscles of the tongue fail to control the flow of saliva leading to drooling.
- The speech is affected and there can be many variations in the speech making it difficult to understand. The speech may become high or low pitched compared to normal, flat, mumbled, slow, fast, slurred, soft or strained.
- The words may come out but articulation is affected so they will not make any sense
Diagnosis of Dysarthria
Difficult or slurring of speech is normally examined by a speech language therapist. They look at the movement of the muscles of the mouth and determine the severity of the problem. To rule out various causes, the therapist will perform simple tests like-
- Making different types of sounds
- Sticking out the tongue
- Blowing a candle or whistle
- Singing
- Spitting the saliva in the mouth
- Counting numbers etc
Treatment of Dysarthria
Irrespective of the cause of dysarthria, the most beneficial treatment is speech and language therapy. A speech therapist will help you out with the following things:
- Teach you how to talk clearly by taking appropriate pauses and catching your breath so that the words are slow but audible
- Exercises to help strengthen the muscles of your face and jaw
- Voice modulation techniques to make your voice louder
- Using devices like amplifiers to make your voice audible
The following advice or tips can be of much use to a patient with dysarthria. They can help him communicate better and go about his day to day activities.
- Always carry a small book and pen or a smartphone which can become an alternate way of communicating when the other person cannot understand what you are saying.
- Speak slowly and have the full attention of the other person
- Talk face to face. It is easier to see your expressions and lip movements and so communicating becomes more effective.
- When trying to communicate something important, turn down the volume of other devices around you. If you are outside on a noisy road, try using the telephone booth where your voice can be heard well.
- Use short phrases and words
- Take the help of gestures and hand movements.
Multiple Sclerosis and Dysarthria
What causes multiple sclerosis?
Multiple sclerosis (ms) is demyelinating neurological disorder where the myelin sheath covering the nerve cells in the brain and the spinal cord is damaged. As a result the signals from the brain are not communicated effectively to the various parts of the body. This results in loss of bladder and bowel control, weakness of muscles in various parts of the body, paralysis, numbness. It affects the optic nerve and leads to visual disturbances. The disorder makes it appearance between 20 to 40 years of age.
Symptoms of Multiple Sclerosis
When the disorder is in the early stage, the symptoms are vague and not diagnostic but as multiple sclerosis progresses, the diagnosis gets clearer.
- Early signs of ms include clumsiness and difficulty in coordinating movements with tingling and numbness. No two people with multiple sclerosis will have the same symptoms.
- Visual problems are an early symptom of ms. The optic nerve is affected and so the vision tends to become blurred or there may be a gray spot in the vision. Eye pain and transient vision loss may also occur.
- Abnormal sensations are a very common symptoms ms. The patient experiences a sensation as if pins and needles were pricking him. Itching, burning and numbness may also be felt.
- Bladder problems like constant urge to pass urine or difficulty in controlling the urge is common because of weakness of bladder muscles.
- Muscles spasms and a feeling of weakness
- Extreme fatigue and tiredness. This leads to a slowness in work. Even the thinking power of these patients becomes slow.
- Speech problems or dysarthria where the person has a very slow and slurred speech. They have to take along pause between two words and the speech tends to get a nasal twang.
- Lack of concentration and poor memory have been seen in college going students where their academics is seriously affected. Sometimes the problem escalates so much that they are unable to do their day to day tasks.
- Tremors that are felt in the hand.
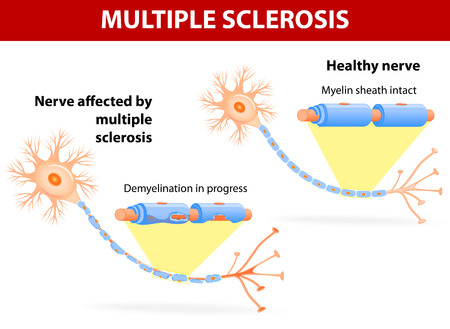
Multiple Sclerosis Diagnosis
The most challenging part is ms diagnosis. There is no single test that can pin point the diagnosis. A neurologist will take a detailed history of the symptoms and their order of appearance. To confirm the diagnosis the following tests may be required.
- MRI of the brain
- Lumbar puncture to check the cerebro-spinal fluid
- Evoke potentials which is an electrical test to check the conduction of the nerves
- Blood tests
Treatment for Multiple Sclerosis
The main aim of the treatment is to slow down the progression of the disease. This is done by using disease modifying drugs that work by suppressing the body’s immune system. MS medications do not cure the disease but they slow down the disease pace and prevent further demyelination of the nerves. The quality of life of the patient tends to improve greatly by use of multiple sclerosis medications.




After my Multiple Sclerosis diagnosis 2 years ago, i stopped all the Multiple sclerosis medicines prescribed due to severe side effects, and decided to go on natural herbal approach. My primary care provider introduced me to Rich Herbs Foundation and i immediately started on their Multiple Sclerosis herbal formula treatment, this herbal treatment has made a tremendous difference for me. My symptoms including shaking, muscle weakness, fatigue, mood swings, numbness, double vision and urinary retention all disappeared after the 4 months treatment! Their website is w w w. richherbsfoundation. c o m. Its just amazing!
My husband will be 85 years old next month and was diagnosed with Parkinson’s disease 16 months ago. his main symptom were and rigidity or stiffness of his right-hand side.he also had some difficulty writing. The original diagnosis was confirmed three months later by a second neurologist. He was on one tablet of pramipexole (Sifrol), 0.25 mg three times a day. Four months ago his neurologist added Biperiden, 2 mg. he takes half a tablet of Biperiden three times a day. He still didn’t feel any better, Since the original diagnosis, his stiffness has slowly increased. He lost touch with reality suspecting it was the medication I took him off the Siferol (with the doctor’s knowledge) and started him on PD natural herbal formula we ordered from NATURAL HERBAL GARDENS, I spoke to few people who used the treatment here in Canada and they all gave a positive response, his symptoms totally declined over a 7 weeks use of the Natural Herbal Gardens Parkinson’s disease natural herbal formula. He is now almost 85 and doing very well, the disease is totally reversed! (Visit their website naturalherbalgardens. c om) I am thankful to nature, herbs are truly gift from God. Share with friends!!