What is Cradle Cap?
Cradle Cap is a skin condition that is seen in babies less than three months of age. The exact appearance of the rash is a crusty, scaly and yellowish flaky lesion seen on the babies scalp. The rash may extend to the corners of the hairline and behind the ears. If a similar flaky lesion is seen in other parts like the eyebrows then it could be seborrhic dermatitis. The appearance may be a cause of worry for many parents and they might feel it is a result of bad hygiene. However it is important to understand that cradle cap is not part of any disease and does not occur as a result of bad hygiene.

Causes of Cradle Cap
Cradle cap is an inflammatory condition that is not a resultant of any kind of bacterial infection or bad hygiene. The two common causes of cradle cap are overactive sebaceous glands and fungal infection of the skin.
In newborn babies, the maternal hormones are still in circulation and so they have an effect on the overactive sebaceous glands in the skin of the baby. This leads to an increased secretion of sebum which is very sticky and it causes the old skin cells to stick to the scalp rather than falling off. This accumulation of sticky sebum dries up with time and forms a crusty yellow layer on the scalp which is called as cradle cap.
Signs and Symptoms of Cradle Cap
- The scalp is most prominently affected. There are yellow, greasy and crusty scales on the head which may shed off. If the condition is very severe, it may look as yellowish patches all over the scalp. If the infant has baby scalp eczema, then the scalp will be affected and there will be a lesion but no crusts or scales.
- There is hair loss as the hair tends to stick to the scabs.
- The child does not feel any itching or discomfort.
- The other sites that may be affected are the eyebrows, eyelids, areas around the nose and groin. Here it needs to be differentiated from similar looking skin conditions like seborrheic psoriasis face and seborrheic dermatitis chest.
If the cradle cap rash is untreated then it may lead to worsening of the symptoms. The crusty lesions may spread to other parts of the body. The baby may develop fungal infection of the mouth (thrush) or ear fungal infection along with cradle cap. Diaper rash is seen in many cases along with fungal infections and cradle cap.
If the crusty lesions become very severe, there can be bleeding at the site where the scales fall off. These raw areas may become a site of more infection and thus the lesion may spread over a large area of the skin. Cradle cap infection may need to be treated using antibiotics.
In few cases, where the immunity is affected, the child may have other symptoms like diarrhoea and frequent infections with dermatitis and cradle cap. These cases need immediate medical attention.
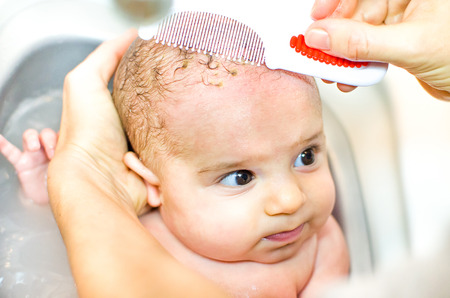
Treatment of Cradle Cap
- In small babies, the cradle cap crusts can be treated by taking good care of the hair and the skin. Shampoo the head more frequently and then in the wet hair use a fine comb and a cotton towel to gently remove the scales. Do not apply too much pressure as it can lead to bleeding and raw areas.
- You may also apply oil to the scalp. Use coconut oil or olive oil and gently massage it on the baby’s scalp. Leave it on for 15 minutes and then gently comb the hair. The oil will help to loosen the scales and make them easy to remove. You can use a fine toothed comb or a clean toothbrush which is soft to remove the crusts. After the oil application, make sure you wash of the oil nicely. If there is too much baby oil on cradle cap, it can add to the secretions by the overactive sebaceous glands and worsen the condition further. Rinse the hair or shampoo them.
- For mild cradle cap, scaling of the crusts is sufficient to take care of the condition. Both these methods should be continued for a week or so for the scales to reduce visibly. If proper care is not taken, it can lead to hair loss as the hair roots stick to crusts and get pulled off.
- For cradle cap ears and cradle cap forehead, you can use the above treatment methods but make sure to remove the crusts using a very soft towel so that the skin is not injured.
- In very severe cases of cradle cap, doctors may suggest the use of anti dandruff shampoos. However they are known to contain substances that cause skin irritation and so should be used only as a last resort.
- If the cradle cap has superadded fungal infection, then an antifungal cream or lotion like clotrimazole may be required. Skin manifestations like yeast dermatitis also respond to anti fungal medications.
- At times the condition persists beyond a few years. The cradle cap in older kids is called as dandruff. In toddlers, the dandruff may be treated with anti dandruff shampoos that are marked safe for children.
Home Remedies: There are a few home based cradle cap remedies for baby. However these treatments are not tested and so they should be tried with caution. Making a paste using baking soda and applying it over the affected area can help to remove the scales. Another home treatment is applying petroleum jelly over the scalp and leaving it overnight. The next morning the crusts soften up and peel off easily.
Differential Diagnosis: The skin condition those are similar to cradle cap like seborrheic dermatitis, dandruff, atopic eczema, dermatitis and psoriasis need to be differentiated well so that the treatment can be effective. The nature of the lesion and its distribution is the most effective way to diagnosing skin pathology.



