About – Cord Blood Banking
During pregnancy, the baby’s umbilical cord is attached to the placenta which is implanted in the wall of the mother’s uterus. The baby derives all the nutrition from the placenta till the time he is born. Immediately after birth, during the second stage of labor, the baby is delivered and the umbilical cord is clamped with two clips and cut. The baby is now a separate entity. During the third stage of labor, the placenta is delivered by spontaneous contraction of the uterus. The blood within the umbilical cord is called cord blood. This umbilical cord blood contains stem cells which are used to treat various disorders as they can grow into organs, blood vessels and tissues. Cord blood banking is the preservation of the baby’s cord blood and isolation of the stem cells which have lifesaving properties for future use. They are preserved by cord blood banks which are similar in operation to a blood bank.
How is Cord Blood Collected?
Cord blood is to be collected immediately after birth. It is a very quick and painless procedure and takes only a few minutes. As soon as the baby is born, the newborn umbilical cord is clamped and cut by the doctor. If there is a delay for more than few minutes then the blood in the cord gets clot and so, it has to be collected fast. A needle is inserted into the umbilical vein of the cord attached to the placenta. The blood drains into a collection bag. Approximately 1 to 5 ounces are collected and the total time taken is about 10 minutes. The blood is then immediately sent to the cord blood bank (cell bank) where detailed testing takes place. The blood is then processed and stored in very low temperature. This process of freezing is called cryopreservation. Recent advances in the medical science are now trying to freeze a part of the umbilical cord itself to isolate the stem cells and study their use in treating diseases. Even placenta banking has gained importance in the recent times and research is underway to know about its contribution in treating various diseases.
Benefits of Stem Cells (Cord Blood Banking)
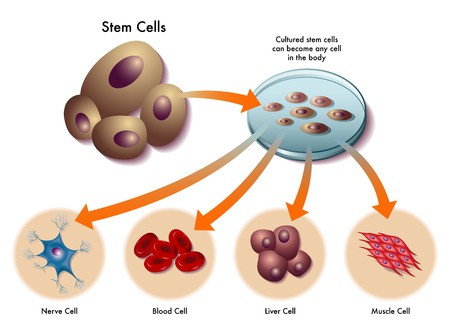
Stem cells are abundantly available and are found in the bone marrow, embryos, fetal tissue, blood and muscles of the body. Every part of the body has some stem cells but they are not sufficient in quantity that they can be harvested for medical or therapeutic use. Cord blood is a very rich source of stem cells which can be easily isolated. They are important structural elements of the immune system. They have the potential to develop into different types of cells so they can be used to regenerate damaged cells and tissues in cases of pathological conditions. This is one of the main reasons why stem cell preservation has gained a lot of importance in the recent times.
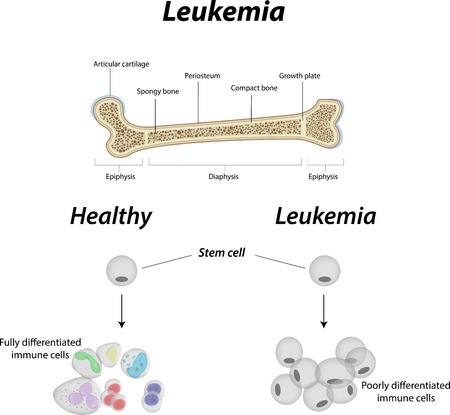
The use of stem cells is tested very well in leukemia. The only line of treatment known is chemotherapy. The disease goes into remission once the diseased cells are destroyed by the chemotherapy. In severe cases or those not responding to treatment, the patients are advised for stem cell transplantation where pleuripotent stem cells are inserted into the body which can stimulate new blood cells and improve the patient’s recovery rates. The stem cells that are found in the peripheral blood are mature whereas the ones in the cord blood are immature so they do not throw up a very strong defense reaction and hence are easier to transplant in patients. The body has a tendency to react or reject any foreign substance entering the body. In cord cells, the rate of rejection is also low.
Diseases That can be Treated with Cord Blood
Cord blood can now be used to treat a number of disorders. Research shows that using the patient’s own cells gives the best results except in some genetic disorders where the defect might be present in the genes. In such cases donor cells may be required.
The diseases that can be treated with cord blood are:
- Blood disorders
- Cancer
- Leukemia
- Aplastic anemia
- Hodgkin’s and Non Hodgkin’s lymphoma
- Thalassemia
- Sickle cell anemia
- Rare metabolic disorders of infants
The most recent study and research is aimed at trying to use the cord blood cells in treating disorders like hydrocephalus, type 1 diabetes (juvenile diabetes) and congenital heart defects. If these trials are successful, cord blood banking may become a mandate for each baby. Currently in many countries it is widely used but not compulsory due to the high cost involved. Stem cell banking cost in India is currently between 20 to 40 thousand rupees.