What is Baker’s Cyst?
Men and women of all ages can suffer from Baker’s cyst. Although this also occurs in children, this Baker cyst is very common in adults. A Baker’s cyst, also known as popliteal cyst is an abnormal collection of too much fluid produced in the sacs of fluid also known as bursa at the back of the knee. This fluid-filled cyst causes a bulge and a feeling of tightness behind one’s knee and further cause severe pain. This cyst was named after the name of Dr. William Morrant Baker, a surgeon who first described it.
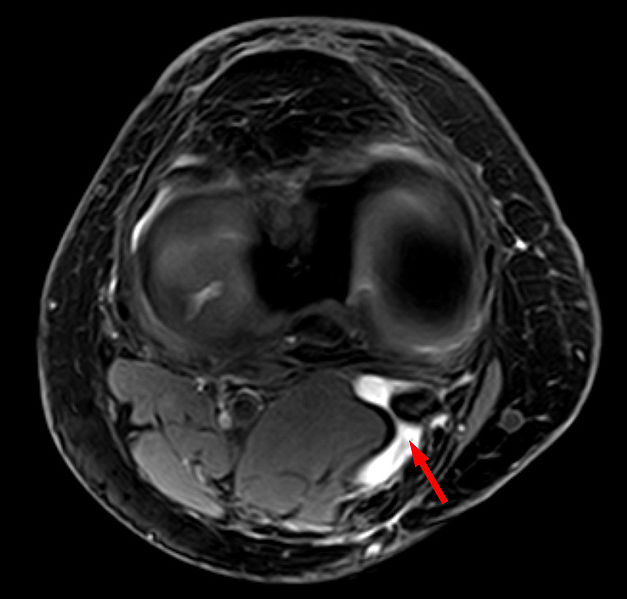
Picture 1: Bakers Cyst
Baker’s Cyst Causes
There are many causes of Baker’s cyst of the knee. As Baker cyst is associated with knee pain, this is commonly cause by swelling of knee joints. Any inflammation of knee joint due to arthritis may lead to Baker’s cyst. The most common arthritis that leads to this is the osteoarthritis which is also known as degenerative arthritis. Another common arthritis that may be associated with Baker’s cyst is the rheumatoid arthritis. Both of which are very common to adults. Another problem that may lead to Baker cyst is a knee injury such as cartilage tears and other knee problems. Other causes like injury or trauma to the knee can also affect fluid build on knee joint that will trigger Baker’s cyst. Local infection can also lead to fluid retention around the knee joint will further result to Baker’s cyst. For no apparent reason, Baker’s cyst can also develop in children and adults
Baker’s Cyst in Children
Baker’s cyst can also occur in children. Children with juvenile arthritis of the knee will most likely be affected by this cyst.
Baker’s Cyst Surgery
In severe cases, Baker’s cyst can rupture and become complicated because of the protrusion of fluid down the leg between the muscles of the calf. In cases like ruptured Baker’s cyst and other severe cases, a Baker’s cyst surgery is important. A Baker’s cyst surgery like removing or repairing the torn cartilage will be of great help to address the problem. In some conditions, if despites of different treatments and therapies, the overproduction of fluids recur, the Baker’s cyst will be removed through a surgical procedure. However, a patient should undergo several pre-operating procedures before a surgical operation be facilitated. These procedures should include physical examination. A medical history is also important to track the records of a patient to avoid further complications eventually. A join x-ray will also be of help to show the presence of arthritis in the knee joint. Transillumination and Magnetic Resonance Imaging or MRI as well as Ultrasound are also important to evaluate the patient’s knee joint’s condition.
Baker’s Cyst Complications
It is true that Baker’s cyst normally do not require treatment and patients do overcome this in due time especially if the symptoms are just mild. However, there are some conditions that may lead to further complications if not properly addressed or treated. Some of the complications of Baker’s cyst if remain untreated may include the following:
- The swelling and pain will worsen as the cyst continues to grow.
- The cyst may go down the legs into the calf muscles which are more threatening and painful.
- Ruptured Baker’s cyst may occur as the cyst can burst. This will further cause bruises on the ankle of the affected leg because of the fluid leaks. If this thing happens, this needs immediate medical attention and evaluation.
Baker’s Cyst Treatment
Baker’s cyst recovery time cannot be determined but can be treated easily. Some of the treatments may include:
- As the underlying cause of Baker’s cyst is arthritis, treatment for arthritis should be applied.
- It is also better if a person observing several symptoms related to Baker’s cyst should refrain or temporarily restrain physical activities that use knee joint.
- Apply cold compress such as ice packs will also ease the pain and swelling.
- Uses of crutches and other aids to help a patient not to put too much pressure on knee joint will be of advantage.
- It is also important to have exercises to stretch out the bones and knee joint as well as muscles. This will reduce the symptoms and preserve knee function.
- In some cases cortisone injections will be applicable. A corticosteroid will be injected into the knee to reduce the inflammation. However, this may just relieve the pain but not prevent the cyst from recurring.
- Draining the fluid from knee joint using a needle under the ultrasound guidance may also applicable.
References:
http://www.mayoclinic.com/health/bakers-cyst/DS00448
‘s_cyst?OpenDocument