What is Amniocentesis?
Amniocentesis is a diagnostic procedure where the amniotic fluid surrounding the baby is studied to determine the possibility of chromosomal abnormalities in the growing fetus. It is commonly called as the needle pregnancy test. Can an amniocentesis determine the gender? It can be used to determine the sex of the fetus and hence it is not permitted in some countries where prenatal sex determination is a criminal offence. It is carried out between 16 to 20 weeks of pregnancy (amniocentesis after 20 weeks is usually not preferred due to the increased risk on the fetus). It is an invasive test and also carries a very small risk of miscarriage. It is indicated in those cases where the preliminary tests like triple marker test or quadruple test are suggestive or show a high risk result. In such cases or in ladies with a history of genetic anomaly in the previous baby, this test is indicated.
Amniocentesis Procedure
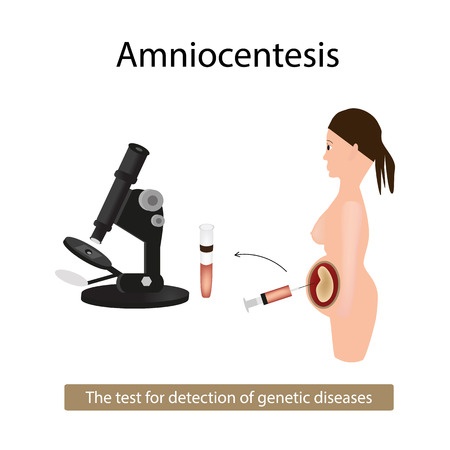
The procedure is done under local anesthesia. You need to lie down on your abdomen. The area to be pricked is cleaned with an antiseptic solution. The doctor performs a sonography to assess the position of the baby. Under continuous ultrasound guidance, a needle is inserted which punctures the skin and uterine wall. It then enters the amniotic sac and 20 ml of the fluid is drawn with the needle. Fetal cells are separated from the sample and are fixed and stained. The sample gives rise to a karyotype-chromosomal picture of the fetus. Then the chromosomes are examined under the microscope for chromosomal defects which may be suggestive of diseases like Down’s syndrome, Edward’s syndrome and Turners syndrome. The puncture over the skin heals on its own. The extracted amount of amniotic fluid is replenished on its own within 48 hours. At the end of the procedure the fetal heart rate is monitored and other parameters are checked to assess fetal well being.
Indications of Amniocentesis
This procedure is carried out in the following conditions:
- Ultrasound results suggestive of structural defects in the growing fetus
- Parents are carriers of recessive genetic disorders like sickle cell disease, cystic fibrosis etc
- History of genetic disorders in the previous baby like Down’s syndrome, Edward’s syndrome, Turners syndrome, Neural tube defects.
- Age – Mothers age over 35 years is a risk factor and demands screening for genetic disorders.
- Family history of a genetic disease or diagnosed chromosomal disease in the spouse.
- To diagnose an intrauterine infection
- To check if the baby has Rh incompatibility. This is a condition where there is an incompatibility between the maternal and fetal blood.
- To assess the lung maturity status of the fetus. This is done by checking for the presence of surfactant in the amniotic fluid.
- To screen for rare inherited metabolic disorders.
This test however cannot diagnose certain disorders like cleft lip or cleft palate. These structural defects are studied in the pregnancy ultrasound by doing an anomaly scan around 20 weeks of pregnancy. A 3d ultrasound pregnancy clearly shows you such defects if present in the fetus.
Risks and Complications Associated with Amniocentesis
Talking about complications in the procedure of amniocentesis risk of miscarriage is always present. But there are no known studies to suggest it. Also the risk associated is very low. Many ladies may miscarry in the second trimester anyway without being subjected to the procedure.
The procedure is normally carried out between the 16 to 20th week of pregnancy. Before this there is a risk of injury to the growing fetus. Hence early amniocentisis is not recommended. The only way to reduce the risk is to do the procedure at a hospital by a registered medical practitioner under ultrasound guidance. When the needle is inserted by viewing the baby by ultrasound, chances of fetal injury are very low.
Some known complications which may occur from this procedure are preterm labor, respiratory distress, postural defects and fetal injury. Another procedure which is known as CVS-Chorionic Villus Sampling has a much lower risk and is done four weeks prior to amniocentesis. It is preferred as a diagnostic tool in cases where the possibility of genetic defects is much higher.
Results of Amniocentesis

You can get the full results of the procedure in about one to two weeks. Generally triple marker test to assess the levels of AFP-Alpha Foeto Protein are also done along with this test to get a more accurate result.
You will be able to meet with a genetic counselor once you have the test results who will tell you the prognosis and future course of action. The condition of the baby and the anticipated risks will also be explained to you.