What is Arthritis?
Arthritis is commonly understood as joint pains. The meaning lies in the word itself “arthro” meaning joint and “itis” meaning inflammation. Hence, it is actually inflammation occurring in any joint of the body. It is a common disease and can affect men, women and children. However, it is seen more commonly in the older age group. The symptoms of arthritis are pain, swelling, decreased mobility and stiffness of the affected joint. Associated arthritis symptoms will be present depending on the type of arthritis. Let us learn in detail about the various types of this condition.
Types of Arthritis
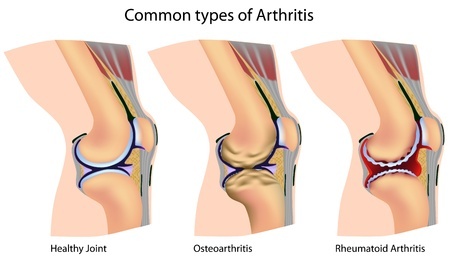
Degenerative Arthritis – Osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis is the commonest presentation of arthritis. It affects the large joints of the body like the knee joints. The joint cavity has two ends of long bones with a layer of cartilage in the middle that acts as cushion and helps in smooth and painless movements. With advancing age, this cartilage begins to wear off and the friction between the bony ends causes arthritis pain on movement. It is an age related phenomenon but there are some risk factors like obesity, family history and previous injury to the knee joint which tend to advance the degenerative process and cause early onset of symptoms of arthritis.
Inflammatory Arthritis – Rheumatoid Arthritis
Rheumatoid Arthritis is a type of autoimmune polyarthritis. In normal conditions, the immune system of the body acts as a protective machinery for the body, but in autoimmune diseases it begins to work against the body. The immune cells from the blood enter the joint cavity and trigger an inflammatory reaction. It is genetic in origin and smoking is identified as a risk factor. Due to the inflammation there is pain, redness and swelling of the joint. Ultimately the ends of the bone are damaged and it may lead to permanent disability if the disease is not checked in time. It affects the smaller joints like the joints of hands, fingers, wrist etc bilaterally (both sides of the body). Early diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis symptoms and treatment using disease modifying drugs (DMARDs) is vital in all cases of rheumatoid arthritis.
Metabolic Arthritis – Gout
Gout or Gouty arthritis is commonly known to affect the first metatarsal joint of the foot, the great toe. The main reason is the inability of the body to get rid of uric acid which is formed as a result of protein metabolism. The excess amounts of uric acid get deposited in the form of crystals in the joint cavity and lead to inflammation and severe pain. The most important part of treating this type of arthritis is diet modification. Following a proper arthritis diet, with restriction on protein intake and high protein foods along with medications helps to bring down the levels of uric acid effectively.
Infectious Arthritis
This type of arthritis occurs when a bacteria or virus enters the joint and causes inflammation or in patients suffering from psoriasis (psoriatic arthritis). It is seen in food poisoning by salmonella, gonorrhea (STDs) and blood to blood infections like hepatitis-C. They are mostly acute infections and can be well treated with antibiotics.
Signs and Symptoms of Arthritis
The signs and symptoms of arthritis are very common but are at times overlooked by the patients. Understanding the symptoms at the right time and getting medical help for the disease can save you from bone deformities and related health problems. However, following the right treatment and medications will only help in easing off the pain and help avoid deformities to only a small extent. Here are the common arthritis symptoms you should look out for:
- Joint pain
- Redness and swelling of affected joint
- Stiffness – It is one of the major symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis. The stiffness is classically presented as bilateral and most severe for the first one hour after waking, reducing on movement. In osteoarthritis the stiffness is more on first motion and after a period of rest. It is unilateral.
- Reduced mobility
- Restriction in the range of movement of the joint
- Change in the gait (limping or wobbling gait)
- Deformities in joints are seen in severe cases of Rheumatoid Arthritis
Diagnosis of Arthritis
Diagnosis is made on the basis of a detailed history and physical examination of the affected joint. X-ray and blood tests are used to confirm the diagnosis.
- Osteoarthritis is confirmed on X-ray by reduced joint space (worn out cartilage), bony spurs and osteophytes.
- Rheumatoid arthritis is confirmed by blood test which shows positive RF (Rheumatoid factor)
- Blood levels of uric acid above normal confirm diagnosis of gout.
- Joint aspiration is used to rule out the other types of arthritis.
Arthritis Treatment
The main aim of treating arthritis is joint pain relief and preserving the joints. Osteoarthritis treatment mainly includes symptomatic arthritis pain relief via pain killers. DMARDs are used for Rheumatism. The most important part of treatment is occupational therapy, which is learning to live with arthritis in a way that you do not cause further damage to the joint by your day to day activities.
- Using support bars and handles in the washrooms
- Use of braces and walkers to avoid straining the joints
- Avoiding positions that strain your joints
- Muscle strengthening exercises.